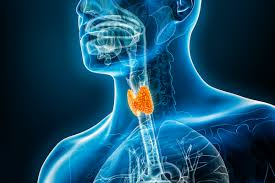
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. From metabolism to growth and development, the thyroid’s influence extends to nearly every cell in the body. Despite its small size, issues with the thyroid can lead to significant health concerns. This article will delve into the anatomy and physiology of the thyroid gland, common disorders associated with it, and the latest technological advancements in its diagnosis and treatment.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Thyroid Gland
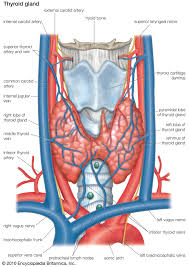
Structure
The thyroid gland is composed of two lobes connected by a narrow isthmus. It is richly vascularized and encased in a fibrous capsule. The gland is made up of thyroid follicles, which are spherical structures filled with colloid, a protein-rich fluid containing thyroglobulin. Follicular cells, which line these follicles, synthesize and secrete thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
Hormone Production
The thyroid gland produces several key hormones:
- Thyroxine (T4): This hormone plays a critical role in regulating metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature. It is the primary hormone produced by the thyroid, with about 90% of the output being T4.
- Triiodothyronine (T3): T3 is more potent than T4 and is responsible for many metabolic processes. Although T3 is produced in smaller quantities, it is the active form that exerts the most influence on the body’s metabolism.
- Calcitonin: Produced by parafollicular cells (C cells), calcitonin helps regulate calcium levels in the blood, promoting the deposition of calcium in the bones.
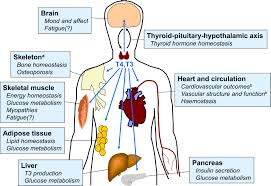
Regulation of Thyroid Function
The production and release of thyroid hormones are regulated by the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. The hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), stimulating the pituitary gland to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH, in turn, stimulates the thyroid to produce T4 and T3. This feedback loop ensures that hormone levels remain balanced and appropriate for the body’s needs.
Common Thyroid Disorders
1. Hypothyroidism
Definition: Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland fails to produce enough hormones, leading to a slowed metabolism.
Causes:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause, where the immune system attacks the thyroid.
- Iodine Deficiency: Inadequate iodine intake can lead to decreased hormone production.
- Medications: Certain medications can interfere with thyroid function.
- Thyroid Surgery: Removal of all or part of the thyroid can lead to hypothyroidism.
Symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Depression
- Dry skin and hair
Diagnosis: Blood tests measuring TSH and free T4 levels are standard for diagnosing hypothyroidism.
Treatment: The primary treatment is levothyroxine, a synthetic form of T4, which is taken daily to normalize hormone levels.
2. Hyperthyroidism
Definition: Hyperthyroidism is characterized by excessive production of thyroid hormones, leading to an accelerated metabolism.
Causes:
- Graves’ Disease: An autoimmune condition that overstimulates the thyroid.
- Thyroid Nodules: Overactive nodules can produce excess hormones.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid may lead to hormone leakage.
Symptoms:
- Weight loss
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Heat intolerance
- Anxiety
- Tremors
Diagnosis: Low TSH and high T4/T3 levels in blood tests indicate hyperthyroidism.
Treatment: Options include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, and sometimes surgery.
3. Goiter
Definition: A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland that can occur in both hypothyroid and hyperthyroid states.
Causes:
- Iodine deficiency
- Autoimmune diseases
- Thyroid nodules
Symptoms: A visible swelling in the neck, difficulty swallowing or breathing if large enough.
Treatment: Depends on the underlying cause; may include hormone replacement or surgery.
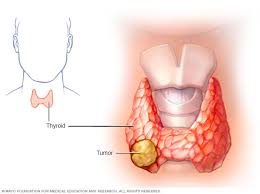
4. Thyroid Nodules
Definition: Nodules are lumps in the thyroid that can be benign or malignant.
Causes: Most nodules are benign, often due to cysts or colloid nodules, but some can be cancerous.
Symptoms: Many nodules are asymptomatic, but larger nodules may cause discomfort or pressure.
Diagnosis: Ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration biopsy are used to evaluate nodules.
Treatment: Benign nodules may only require monitoring, while malignant nodules may necessitate surgery.
5. Thyroid Cancer
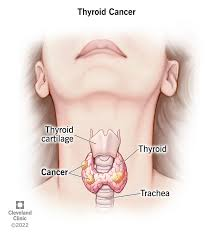
Types:
- Papillary Thyroid Cancer: The most common and generally slow-growing.
- Follicular Thyroid Cancer: More aggressive than papillary but still treatable.
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Arises from C cells and may be hereditary.
- Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: Rare and aggressive, difficult to treat.
Symptoms: A lump in the neck, changes in voice, and difficulty swallowing.
Diagnosis: Ultrasound, blood tests, and biopsies are used for diagnosis.
Treatment: Typically involves surgery, often followed by radioactive iodine therapy.
Technological Advances in Thyroid Diagnosis and Treatment
1. Improved Imaging Techniques
Advancements in imaging technology have significantly improved the diagnosis of thyroid disorders:
- Ultrasound: High-resolution ultrasound has become the first-line imaging modality for evaluating thyroid nodules. It helps determine the size, composition, and vascularity of nodules, guiding further management.
- CT and MRI Scans: These imaging techniques are used in more complex cases to assess the extent of disease, particularly in thyroid cancer.
2. Biomarkers and Blood Tests
The development of new biomarkers is enhancing the accuracy of thyroid disorder diagnoses:
- Thyroid Autoantibodies: Tests for antibodies like TPO (thyroid peroxidase) and thyroglobulin can help diagnose autoimmune thyroid diseases.
- Genetic Testing: In cases of thyroid cancer, genetic testing can identify mutations that guide treatment decisions, particularly in medullary thyroid carcinoma.
3. Minimally Invasive Techniques
Minimally invasive procedures have revolutionized the treatment of thyroid disorders:
- Radiofrequency Ablation: This technique uses heat to destroy benign thyroid nodules, providing a non-surgical alternative for symptomatic nodules.
- Endoscopic Thyroidectomy: A minimally invasive surgical option that reduces scarring and recovery time.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) is making strides in diagnosing thyroid conditions:
- AI-Enhanced Ultrasound: Machine learning algorithms can assist radiologists in interpreting ultrasound images, improving the detection of malignancies.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze large datasets to identify patterns and predict outcomes, enhancing clinical decision-making.
5. Telemedicine
Telemedicine has become increasingly important in managing thyroid disorders, particularly in remote areas:
- Virtual Consultations: Patients can consult with endocrinologists without the need for travel, making it easier to receive care.
- Remote Monitoring: Patients can use devices to monitor their hormone levels and symptoms, allowing for timely adjustments in treatment.
Conclusion
The thyroid gland is integral to maintaining overall health, influencing metabolism, growth, and development. Understanding its functions and disorders is crucial for effective management. With the rapid advancements in technology, from improved imaging techniques to AI-driven diagnostics, the future of thyroid health looks promising. By leveraging these innovations, healthcare providers can ensure better outcomes for patients with thyroid conditions.
This comprehensive article is designed to rank well on search engines by incorporating relevant keywords and providing valuable information to readers. If you have specific SEO strategies or keywords you’d like to include, let me know!